Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy, is the energy obtained from the heat from the Earth, more precisely of its interior. Geo means Earth and thermal means heat, so geothermal is the heat energy that comes from the Earth.
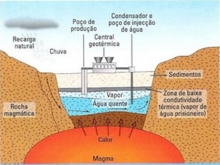
Geothermal energy is heat energy created less than 64 kilometers of the Earth's surface, a layer of rock, called magma, which reaches up to 6,000°C.
The heat of the Earth exist everywhere beneath the surface of the planet, but in some parts is closer to the surface than others, which makes it easier to use. In some places, making holes of just a hundred meters is possible to achieve useful heat.
Typically in the Earth's crust heat increases 25 to 30 centigrade for each kilometre deep toward the center of the Earth.
Geothermal energy has many practical applications, can be used to heat homes, pools, agriculture greenhouses and produce electricity.
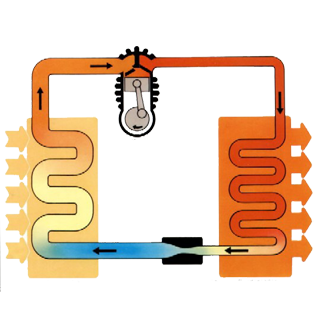
Electrical energy can be obtained through soil drilling in places where there are lot of steam and hot water, these must be drained until the Earth's surface by means of specific pipes. Then the steam is transported to a geothermal power station, which will rotate the blades of a turbine. Finally, the energy obtained by the blade drive (mechanical energy) is converted into electrical power through the generator.
The positive aspects of this type of energy are:
- The emission of pollutant gases (CO2 and SO2) is practically null, not intensifying the greenhouse effect, unlike fossil fuels.
- The area necessary for the installation of the electric central is small.
- Can supply isolated communities.
The negatives aspects:
- Is an energy very expensive and unprofitable because it requires high structural investments and their efficiency is low.
- May result in the exhaustion of the geothermal field.
- The lost heat increases the temperature of the environment.
- The emission of hydrogen sulphide (H2S), extremely corrosive and harmful to health.